
Muscular dystrophy
- Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. It affects both males and females and can manifest in early childhood or later in life.
- The most common type of muscular dystrophy is Duchenne muscular dystrophy, which primarily affects boys and can lead to difficulty walking, breathing, and heart problems.
- Other types of muscular dystrophy include Becker muscular dystrophy, myotonic dystrophy, and facioscapulohumeral dystrophy.
- While there is currently no cure for muscular dystrophy, there are treatments and therapies available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected. Research into potential cures and treatments for muscular dystrophy is ongoing, and there is hope that one day a cure may be found.
- Auto immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle.
- Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune disorder in which antibodies destroy the communication between nerves and muscle, resulting in weakness of the skeletal muscles. Myasthenia gravis affects the voluntary muscles of the body, especially those that control the eyes, mouth, throat and limbs.
- The disease can strike anyone at any age, but is more frequently seen in young women (age 20 and 30) and men aged 50 and older.
Tetany
- It is a medical condition characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, which can lead to muscle spasms, cramps, and stiffness.
- It is caused by low levels of calcium in the blood, which can be caused by a variety of factors such as hypoparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, or even respiratory alkalosis.
- Tetany can affect any muscle in the body, but is most commonly seen in the hands and feet.
- It can be a very uncomfortable and painful condition, but it is treatable with medications and supplements to raise calcium levels. If you suspect you may be experiencing tetany, it is important to consult with a medical professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- It means redness and swelling (inflammation) of a joint. A joint is where 2 or more bones meet. There are more than 100 different arthritis diseases. Rheumatic diseases include any condition that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling in joints, muscles, tendons, ligaments, or bones. Arthritis is usually ongoing (chronic).
- Arthritis and other rheumatic diseases are more common in women than men. They are also often linked with old age. But they affect people of all ages.
- Osteoarthritis. This is the most common type of arthritis. It is a chronic disease of the joints, especially the weight-bearing joints of the knee, hip, and spine. It destroys the coating on the ends of bones (cartilage) and narrows the joint space. It can also cause bone overgrowth, bone spurs, and reduced function. It occurs in most people as they age. It may also occur in young people because of an injury or overuse.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. This is an inflammatory disease of the joint linings. The inflammation may affect all of the joints. It can also affect organs such as the heart or lungs.
Osteoporosis
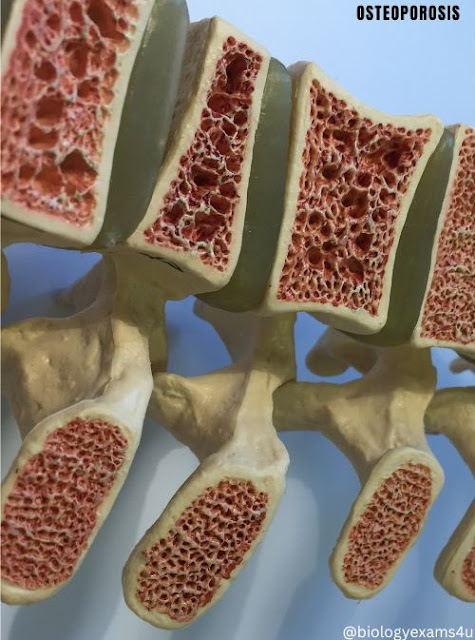
- It is a bone disease that develops when bone mineral density and bone mass decreases, or when the structure and strength of bone changes. This can lead to a decrease in bone strength that can increase the risk of fractures (broken bones).
- It is a “silent” disease because you typically do not have symptoms, and you may not even know you have the disease until you break a bone. Osteoporosis is the major cause of fractures in postmenopausal women and in older men. Fractures can occur in any bone but happen most often in bones of the hip, vertebrae in the spine, and wrist.
Gout
- It is a type of inflammatory arthritis that causes pain and swelling in your joints. It is due to accumulation of uric acid crystals.
- Areas of the body that can be affected by gout include: Joints. Bursae, cushion-like sacs between bones and other soft tissues. Tendon sheaths, membranes that surround tendons. Kidneys, because the high uric acid levels can lead to stones and sometimes kidney damage.
Key Points: Disorders of Muscular and Skeletal System
- Myasthenia gravis: Auto immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle.
- Muscular dystrophy: Progressive degeneration of skeletal muscle mostly due to genetic disorder.
- Tetany: Rapid spasms (wild contractions) in muscle due to low Ca++ in body fluid. Arthritis: Inflammation of joints.
- Osteoporosis: Age-related disorder characterized by decreased bone mass and increased chances of fractures. Decreased levels of estrogen is a common cause.
- Gout: Inflammation of joints due to accumulation of uric acid crystals.
