The phylum Ctenophora takes its name from two Greek words, ktenos= comb and phora= bearing, as they possess eight combs like plates of locomotion. Ctenophora is a small phylum of marine animals, which are commonly known as comb jellies (sea walnuts) due to their jelly like consistency and comb like locomotory organs. At night they are often bioluminescent. About 60 species of ctenophoran animals are known. The ctenophoran animals are closely allied to coelenterates.
Body
is usually pear shaped (Example: Pleurobrachia) or
ribbon like flat (Cestus).
🎯General Characters of Phylum Ctenophora
- Marine, solitary, free swimming or pelagic.
- No polymorphism and no attached stages.
- Body transparent.
- Cell tissue grade of body organization
Ctenophora Digestive System
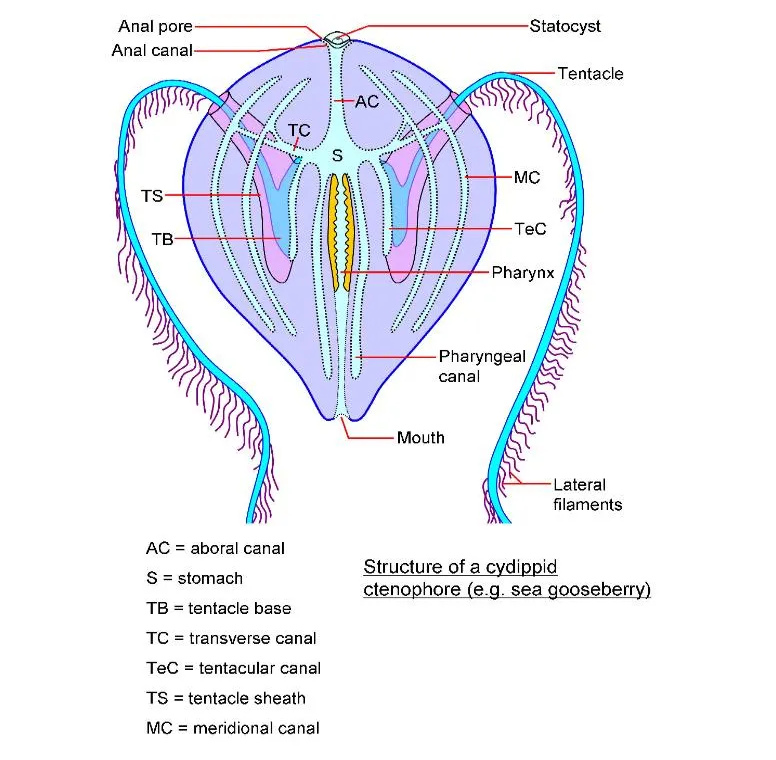
- Digestive system with mouth, stomach, complex gastrovascular canals and two aboral anal pores
- Symmetry biradial along an oral
aboral axis.
- Body acoelomate and triploblastic,
with an outer epidermis, inner gastrodermis and middle jelly like mesogloea
with scattered cells and muscle fibres.
- External surface with eight vertical
rows of comb plates of fused cilia of locomotion. Hence, they are named comb
jellies.
- A pair of long, solid, retractile
tentacles present.
🎯Unique Features of Ctenophora
- Comb like ciliary plates for
swimming.
- Special adhesive cells, the colloblasts for
capturing the prey
- Two anal pores.
- Mesogloea with amoebocytes and smooth muscle cells
- Nematocysts absent. Instead, special
adhesive and sensory cells, called colloblasts, present on tentacles, help in
food capture. Skeletal, circulatory, respiratory and excretory organs absent.
- Nervous system diffuses. Aboral ends
bears a sensory organ, the statocyst.
- All monoecious(hermaphrodite). Gonads
develop side by side on digestive canals and develop from endoderm.
- Development of ctenophores usually
includes a characteristic cydippid larva.
- Alternation of generation and asexual
reproduction absent.
- Regeneration and Paedogenesis common.
🎯Classification of Phylum Ctenophora
Phylum Ctenophora grouped into two classes: Class Tentaculata and Class Nuda

- Pleurobrachia
- Ctenoplana
- Beroe
- Mnemiopsis
- Bolinopsis


.png)