What is CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing?
CRISPR/Cas9 is a gene-editing tool used to modify, delete, or correct specific regions of DNA.
It is faster, cheaper, and more accurate than previous techniques of editing DNA, and it has a wide range of potential applications.
CRISPR/Cas9 stands for?
CRISPER Stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats: These are short repetitive palindromic DNA sequences present in a genome
Cas 9: Cas9 is a CRISPR-associated (Cas) endonuclease, that cut DNA at a location specified by a guide RNA.
The system was originally discovered in bacteria as a defense mechanism against viral attacks.
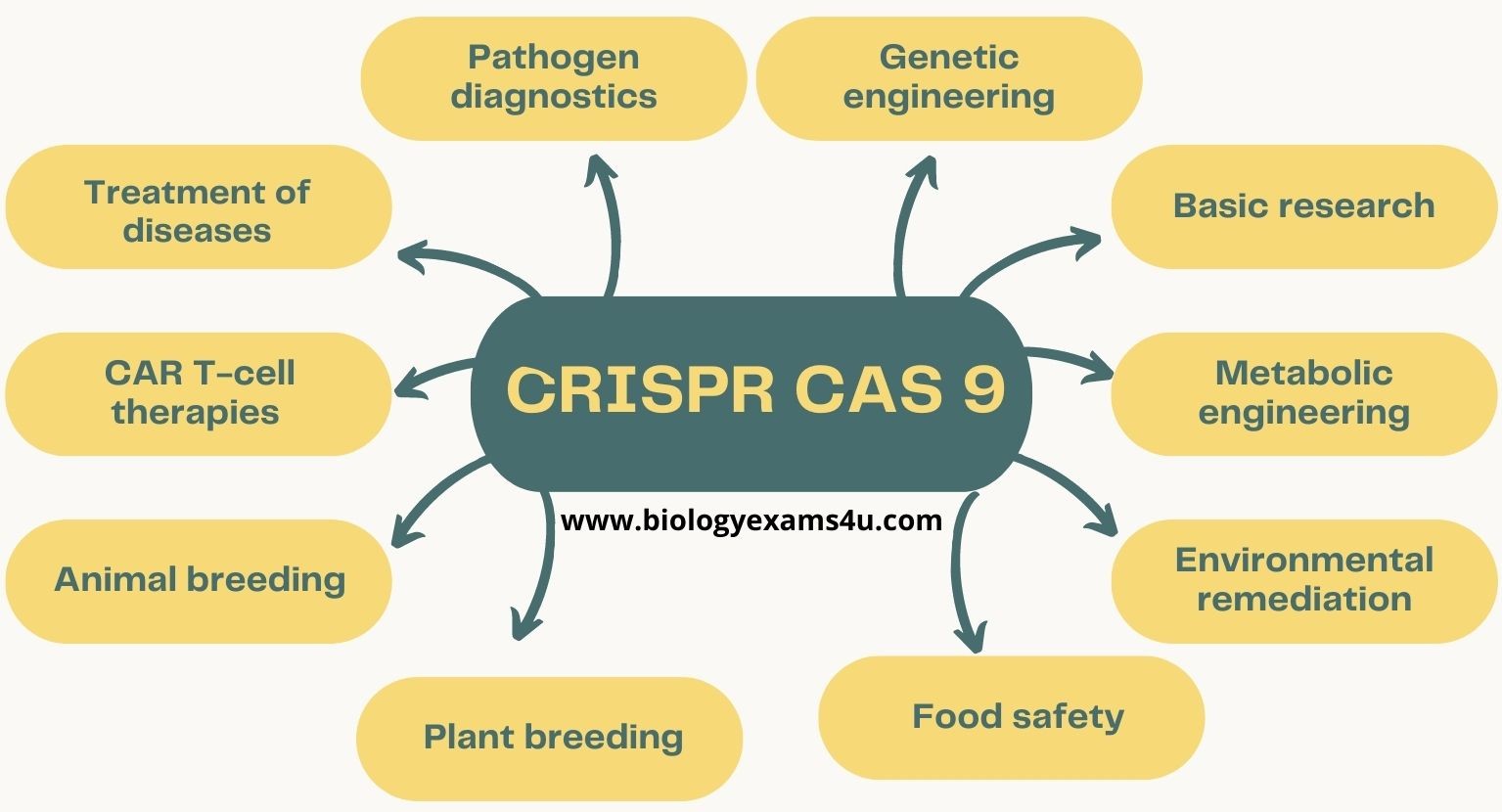
What are the applications of CRISPR CAS9 Technology?
1. Treatment of diseases: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to treat a wide range of diseases, including cancer, sickle cell disease, and HIV.
- For example, CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to target and destroy cancer cells, or to insert a healthy copy of a gene into a cell that is missing or defective.
- CRISPR-Cas9 is used to screen thousands of genes implicated in tumor-formation in mice by gene knockout method
2. Pathogen diagnostics
CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to identify different strains of pathogens quickly and cheaply.
The SHERLOCK (Specific High-sensitivity Enzymatic Reporter unlocking) a CRISPR bases platform can detect viruses, bacteria, or other targets in clinical samples such as urine or blood, and reveal results on a paper strip — without the need for extensive specialized equipment. This technology has been used to differentiate between African and American strains of the Zika virus.
3. Genetic engineering: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to engineer crops and livestock with improved traits, such as resistance to pests or disease.
- For example, CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to create crops that are more nutritious or that produce higher yields.
4. Basic research: CRISPR-Cas9 is a powerful tool for basic research, and it is being used to study a wide range of biological processes, such as development, cell differentiation, and disease.
- For example, CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to identify the genes that are involved in a particular disease or to track the development of a cell or organism or to study the function of a gene by gene knockout method.
5. Metabolic engineering and Bioproduction: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to produce proteins and other biomolecules in a more efficient and cost-effective way.
- For example, CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to produce vaccines, antibodies, and other therapeutic proteins.
- CRISPR with nuclease-deficient endonucleases with transcription factors is used to activate or repress gene expression to alter an organism's metabolism to produce economically important chemicals and biofuels from cheap starting materials, such as sugars.
6. Environmental remediation: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to clean up environmental pollution, such as by targeting genes that are responsible for the production of pollutants.
- For example, CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to remove genes that are responsible for the production of oil from oil spills.
7. Food safety: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to improve food safety by targeting and silencing genes that are responsible for the production of toxins or allergens.
- For example, CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to remove genes that are responsible for the production of aflatoxins, which are a type of toxin that can be found in peanuts.
8. Plant breeding: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to improve plant breeding by targeting genes that are responsible for traits such as yield, resistance to pests and diseases, and nutritional content.
- For example, CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to create plants that are more resistant to drought or that contain higher levels of vitamins.
9. Animal breeding: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to improve animal breeding by targeting genes that are responsible for traits such as growth rate, disease resistance, and milk production. There are numerous ethical concerns related to the genetic modification of livestock for consumption.
- For example, CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to create animals that grow faster or that produce more milk.