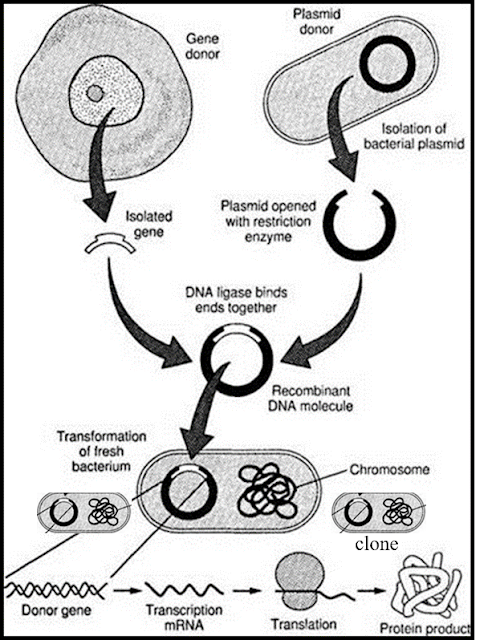
What is Gene Cloning?
Gene Cloning or
molecular cloning is the process of making many identical copies of a DNA
fragment or gene.
Applications of Gene
cloning
- Study of gene structure and function
- If it is a newly studied gene; Gene cloning followed by DNA sequencing helps us to understand the structure of the gene.
- Mutagenesis to understand the function of the cloned gene.
- Expression of cloned gene is preferred if the gene codes for some therapeutically important proteins like insulin.
Step 1: Identification &
Isolation of Gene of interest or DNA fragment to be cloned.
Step 2: Insertion of this
isolated gene in a suitable vector.
Step 3: Introduction of this
vector into a suitable organism/ cell called host (transformation).
Step 4: Selection of the transformed
host cell.
Step 5: Multiplication or expression of the introduced gene in the host.
Step1: Identification and isolation of gene of interest
From where we get the desired gene?
If we are studying a gene
or a DNA fragment for the first time, we need to construct a genomic library
From
- Genomic library
- cDNA library
- Chemical synthesis and PCR amplification of the gene is possible only if we know the sequence of the gene to make relevant primers.
Step II: joining of
this gene into a suitable vector (construction of recombinant DNA)
What is a Gene Cloning Vector?
A vector is any DNA molecule which is capable of multiplying inside the host to which our gene of interest is integrated for cloning. The selection of vector depends upon the size of the fragments to be cloned.
Common vectors include plasmids (Eg: pBR 322) and phage vectors.
In the process,
restriction enzymes functions as scissors for cutting DNA molecules. Ligase
enzyme is the joining enzyme that joins the vector DNA with gene of interest by
forming phosphodiester bond. The resulting DNA is called the recombinant DNA,
chimera or recombinant vector.
Step III: Introduction
of this vector into a suitable organism
Introduction of
recombinant vector into host cell is achieved by different gene transfer
methods. The process is called transformation
a. Physical gene transfer methods:
- Electroporation
- Microinjection
- Liposome mediated gene transfer
- Silicon Carbide fibre mediated gene transfer
- Ultrasound mediated gene transfer
- DNA transfer via pollen
b. Chemical gene transfer methods:
- Poly Ethylene Glycol mediated (PEG mediated),
- Calcium Chloride mediated
- DEAE dextran mediated gene transfer
c. DNA imbibition by
cells, tissues or organs: Transformation
d. Agrobacterium mediated
gene transfer in plants
e. Virus mediated gene
transfer: Transduction
Step VI: Selection of
transformed recombinant cells with gene of interest
The number of cells with recombinant vector will be very less. So the next step is to select the transformed recombinant cells with our gene of interest from the sea of non-transformed cells. Several methods are employed for selection of transformed cells:
- Antibiotic resistance medium
- Visible characters,
- Assay for biological activity,
- Colony hybridization,
- Blotting test.
The selected cells are
cultured in large scale.
Step V: Multiplication
or expression of the gene of interest
The objective of gene
cloning is either to make numerous copies of the desired gene or to produce the
protein coded by the desired gene. The inserted gene along with the vector will
replicate inside the host so that many copies of the desired gene is
synthesized. This process of making many copies of the desired gene or DNA fragment
is called gene cloning.
For expression of the
desired gene, expression vector is used (vector with control elements like
promoter, operator etc. The product is synthesized in bioreactors; large
culture vessels for large scale production.
A great way to thank and support us.
- Visit our TpT store by clicking here.
- Download free resources or
purchase some.
- Please rate the product and
follow us on store.
Thank you so much