This is a microchromatographic method supplementing paper, column and ion-exchange chromatography. In this method, a glass plate or some other supports is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent which adheres to the plate. The thin layer represents an open column. The sample (pigments, etc.) is spotted on this coating as a solution and is developed in a trough containing the appropriate solvent (ascending). The most common coating applied is that of silica gel containing CaSO4, which acts as a binder.
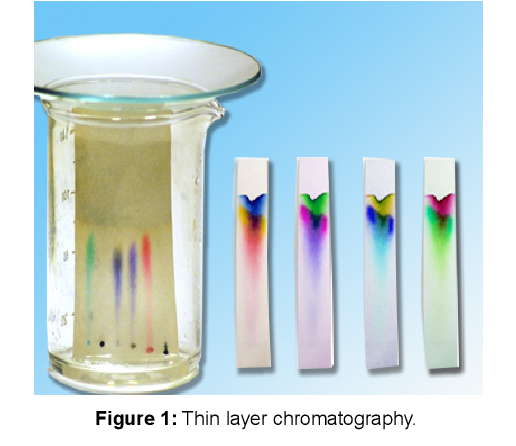
This method has certain selective advantages:
(1) It provides a much quicker development than paper column or chromatography (the separation time may range between 20 and 40 minutes).
(2) Besides, the separation is much sharper than in paper or column chromatography.
(3) It is an extremely sensitive method(about 100times more sensitive than paper chromatography)
4) It is sort of tracer techniques requiring a diminishingly small quantity of material (as low as 0.5ug)
