Which is the largest antibody? IgM
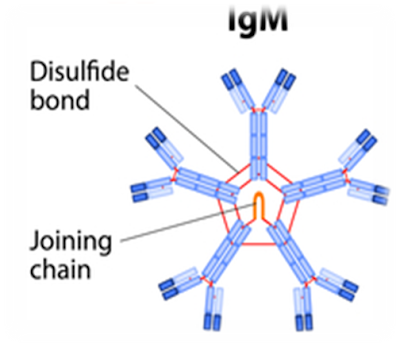
Structure: 5-H2L2 units + 1 J chain (joining chain)
a ‘pentamer’(made of 5 H2L2
monomers) composed of 10 μ-heavy chains, 10 light chains, and a single J chain
linked by inter-μ chain disulfide bonds. It is a macroglobulin.
Heavy Chain: µ (IgM)
Antigen binding sites:10, therefore the most effective
antibody
MW: ~9,00000 D
% in serum: ~6%
Functions of IgM:
Crosses placenta: no
Fixes complement: Yes
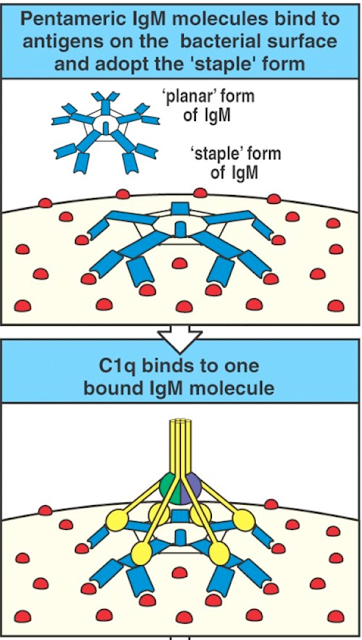
How IgM fixes complement?
Fc region of IgM bound
infected cells can activate complement proteins (set of serum proteins involved
in first line of defense) that works in cascade activating many other complement
proteins finally causing destruction of infected cells by enhancing phagocytosis
by phagocytes or by the formation of membrane attacking complex (MAC) causing
the destruction of infected cell (See the figure).
Which is the first Antibody produced in immune response?
IgM, Predominant in primary immune response along with IgG
- Neutralization (IgG covers toxins of pathogens by close binding, thereby causes neutralization)
- Agglutination (causes clumping of pathogens like bacteria which are later cleared out by phagocytes),
- Complement activation, opsonization (binding of IgG to infected cells acts as a signal for phagocytes, thus enhancing the phagocytosis by phagocytes)
- Monomer functions as B cell receptor
- IgM mediates Type II hypersensitivity
5 Classes of Immunoglobulins