- Laboratory:
Cavendish laboratory
- Other major contributors: Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin of Kings College,
London provided the x-ray crystallographic data.from that data Watson and
crick got the idea of DNA double helix
- Phobeus
Levene proposed the Tetra nucleotide theory and Linus Pauling's triple
helix model. Both these even though wrong provided many clues regarding
the DNA structure
- Erwin
Chargaff of Columbia University proposed the complementarity of base pairing.
Watson
and Crick applied this for orienting base pairs within DNA
double helix and proposes a DNa copying mechanism based on this data.
10 Salient Features of DNA double helix model
1.
DNA is made up of two
strands that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix, called
a double helix.
2.
The 2 strands are
anti-parallel; one strand has 3′ C of sugar woth –OH in the “upward”
position, and the other strand has 5′ C with P in the upward position
3.
Each strand is made up
of deoxyribonucleotides joined by phosphodiester bond
4.
Sugar and Phosphate forms
the backbone of DNA strand
5.
The two strands are held
together by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases
6.
Base Complementarity
Relationship (Chargaff’s Rule)
Adenine pairs with
Thymine by 2 H bonds
Guanine pairs with
Cytosine by 3 H bonds
See more Chargaffs Experiment and Chargaffs Rule
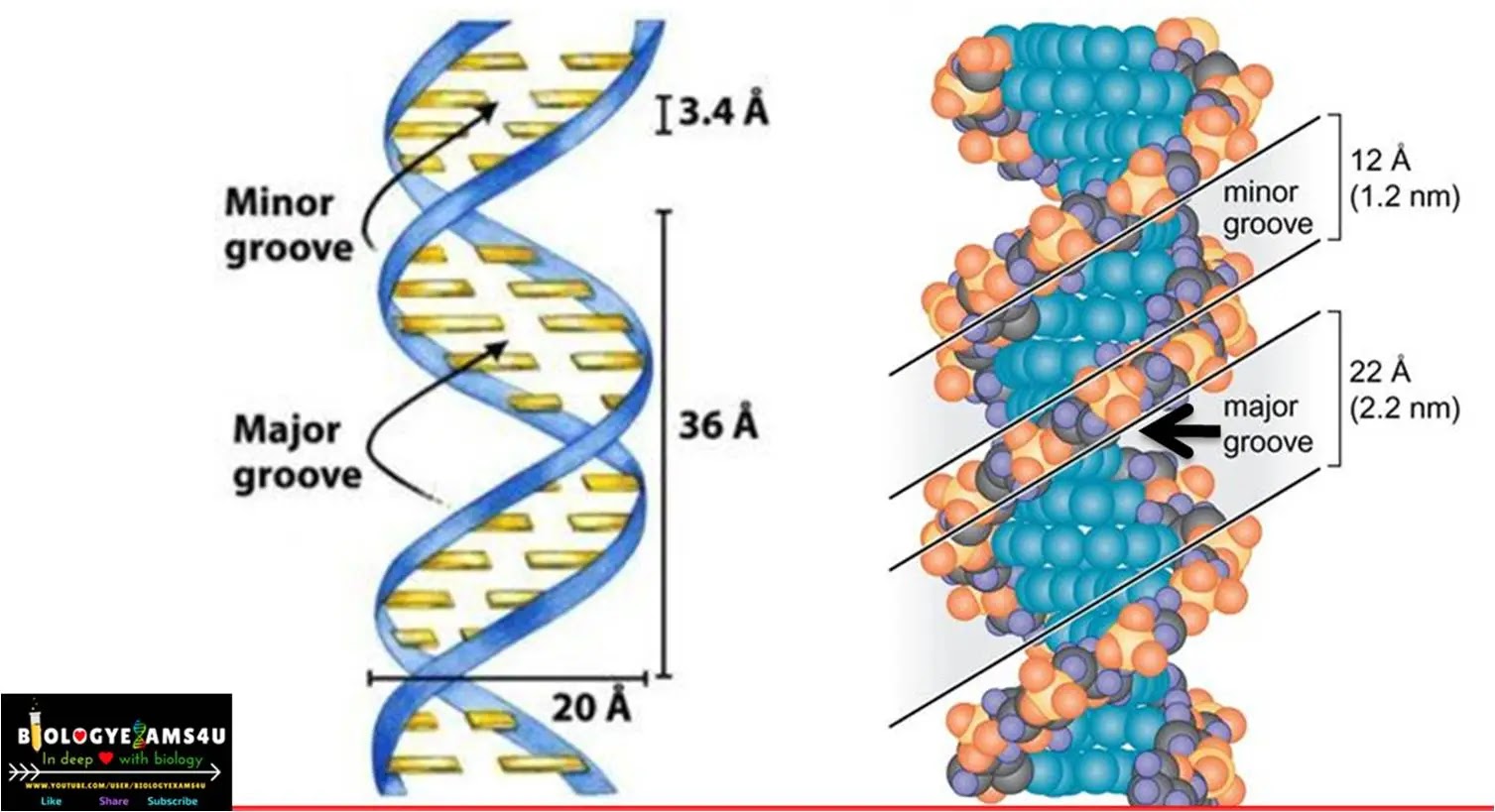
7.
DNA contain 2 grooves,
called the major groove and the minor groove. Major
groove is wide and deep and minor groove is narrow and shallow.
DNA Dimensions
8.
The diameter of the
double helix is 2 nm (20 A0)
9.
Distance btw adjacent
base pairs is 0.34 nm (3.4 A0)
10.
There are ~10 nucleotide
base pairs per turn of helix
1 turn=0.34x10=3.4 nm
(34 A0)
This is a summarized video on DNA Double Helix Model of Watson and Crick



Useful
ReplyDeleteVery easy , thanks
ReplyDelete