1. Which of the following is incorrect about Keystone
species?
(CSIR
UGC NET LIFE Science Dec 2017)
a. Species other
than consumers can be a keystone species
b.Keystone species
has influence on a community proportionate to its abundance
c.Removing a
keystone species can reduce species richness of a community
d. Removing a
keystone species can effect successive trophic levels causing a trophic cascade
Ans: 2.Keystone species has influence on a community proportionate to its abundance
•A flagship species is a species
selected to act as an ambassador, icon or symbol for a defined habitat, issue, campaign or
environmental cause.
•Eg: panda WWF, Bengal
Tiger, African elephant, Asian Elephant, Golden Lion Tamarin
•Umbrella species: Species that have
either large habitat needs or other requirements whose conservation results in
many other species being conserved at the ecosystem or landscape level.
•Eg: Tiger; Efforts
have been made to save the populations of wild Tigers in order to save
other species that are
present in the same ecosystems such as Leopards, Monkey, Hares, Boars, etc
•
Endemic species are plants and animals that exist
only in one geographic region.
•Eg: tortoises of the
Galápagos , Kangaroos in Australia, Asiatic Lion, Neelgiri Tahr Etc Strobilanthes kunthiana endemic to southern
western Ghats
.
2. A species whose
life history strategies allow for high intrinsic rates of increase (r
strategist) will also exhibit the following EXCEPT
(CSIR UGC NET LIFEScience
Dec 2017)
a.
high tolerance for both environmental instability and low quality resources.
b.
short period of exponential population growth (r)
c.
reproductive strategy that involves random mating, semelparity and little or no
parental investment
d.
survivorship that show density-dependent mortality, typically exhibiting Type 1
or 2 survivorship curves
Ans: d. survivorship that show density-dependent mortality, typically exhibiting Type 1 or 2 survivorship curves
3. In the context of
diversity patterns of species, which one of the following statements is
INCORRECT?
(CSIR
UGC NET LIFEScience
Dec 2017)
a. Alpha diversity is diversity within a single community
b. Beta diversity is a measure of the change in species composition from one
community or habitat to another
c.Alpha diversity is the regional diversity found among range of communities in a
geographical region
d. Gamma diversity is the regional diversity found among range of
communities/habitats in a geographical region
4. Given
below is an ecological pyramid. The above pyramid represents:
(CSIR
UGC NET LIFEScience
Dec 2017)
a. Pyramid of number
of a parasitic food chain and pyramid of biomass of a pond ecosystem
b. Pyramid of
number of a pond ecosystem and pyramid of biomass of a forest ecosystem
c. Pyramid of energy
of a grassland and pyramid of biomass of an open ocean ecosystem
d. Pyramid of
biomass of a grassland and pyramid of number of a tropical forest ecosystem
Ans: a. Pyramid of number of a parasitic food chain and pyramid of biomass of a pond ecosystem
5. Three species M, N and O when grown independently in a laboratory showed typical logistic growth curves. However, when grown in pairs, the following growth curves were observed. What interpretation regarding the interspecific relationship between M, N and O can be deduced from the above observations?
5. Three species M, N and O when grown independently in a laboratory showed typical logistic growth curves. However, when grown in pairs, the following growth curves were observed. What interpretation regarding the interspecific relationship between M, N and O can be deduced from the above observations?
a.
N predates over O and therefore can also predate on M.
b.
N is competed out by M and O.
c.
N and O possibly have a prey-predator relationship.
d. M and O exhibit
prey-predator relationship
Ans: c. N and O possibly have a prey-predator relationship.
6. Given below are the population pyramids of three different populations A, B and C depicting the relationship between birth and death rates in each. Based on the population pyramids given above, which one of the following is INCORRECT?
(CSIR UGC NET LIFE Science Dec 2017)
a. Population B has slower growth rate than population A.
b. Population C has birth rate higher than its death rate.
c. Population A represents a rapidly growing population.
d. Population B has the highest death rate among the three populations.
Ans:b. Population C has birth rate higher than its death rate.
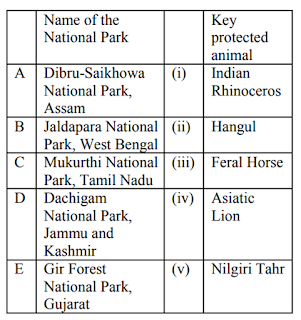
7. Given below are names of some of the National Parks of India and their key protected animals. Based on the table given above, which of the following options represents the correct match?
(CSIR UGC NET LIFE Science Dec 2017)
a. A-(iii); B-(i); C-(iv); D-(ii); E-(v)
b. A-(i); B-(ii); C-(v); D-(iii); E-(iv)
c. A-(i); B-(ii); C-(iii); D-(iv); E-(v)
d. A-(iii); B-(i); C-(v); D-(ii); E-(iv)
Ans: d. A-(iii); B-(i); C-(v); D-(ii); E-(iv)
8. Given below are two patterns of ecological succession. Four species are represented by A, B, C and D. An arrow indicates “is replaced by”. In the context of ecological succession, which of the following statements is INCORRECT with respect to the figures given above
(CSIR UGC NET LIFEScience Dec 2017)
a. Model – X represents facilitation model and Model - Y represents tolerance model.
b. Model – X represents tolerance model and Model – Y represents inhibition model.
c. As per Model – Y, C can out-compete B but can also invade a habitat in their absence.
d. As per the Model – X, A makes the environments more suitable for B to invade.
Ans: b. Model – X represents tolerance model and Model – Y represents inhibition model.
9. Given below are the species accumulation curves and rarefaction curves measured in an ecological community. Which one of the following statements is INCORRECT about the two curves?
(CSIR UGC NET LIFEScience Dec 2017)
(CSIR UGC NET LIFEScience Dec 2017)
1. Species accumulation curve moves from left to right and rarefaction curve moves from right to left.
2. Species accumulation curve represents the total species richness of the assemblage.
3. Rarefaction curve represents the mean of repeated resampling of all pooled samples.
4. Rarefaction curve is the realized accumulation value of the total species in a community
Ans: 4. Rarefaction curve is the realized accumulation value of the total species in a community




nice
ReplyDelete