Eukaryotic Protein Synthesis vs Prokaryotic Protein Synthesis
1. In eukaryotes protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm.
In prokaryotes protein synthesis begins even before the
transcription of mRNA molecule is completed. This is called coupled
transcription - translation..png)
2. Eukaryotic mRNA molecules are monocistronic, containing the coding sequence only for one polypeptide.
In prokaryotes individual bacterial mRNA molecules are polycistronic having transcripts of several genes of a particular metabolic pathway. (Monocistronic vs polycistronic )
3. In eukaryotes, most of the gene have introns that separate the actual message for the synthesis of one protein into small coding segment called exons.
Prokaryotes do not have introns (Except Archaebacteria).
4. Eukaryotes: The first amino acid methionine entering the ribosome is not formylated.
Prokaryotes: The first amino acid methionine is formylated into N formyl methionine.
5. In eukaryotes, the number of initiating factors (IF) is much more than prokaryotes.
About ten initiating factors(IFs ) have been identified in reticulocytes an RBC. These are eIF1, eIF2, eIF3, eIF4 , eIF5, eIF6 ,eIF4B, eIF4C,eIF4D, eIF4F
Three initiating factors found in prokaryotes. PIF-1 , PIF-2 , PIF-3.
Learn more: Prokaryotic initiating factors and Eukaryotic initiating factors
6. The primary mRNA transcript in eukaryotes undergoes processing and splicing to change into a functional mRNA.
In prokaryotes, splicing of mRNA transcript does not occur.
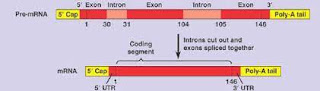
7. In eukaryotes, mRNA molecules are modified by the addition
of a 5’G cap formed of methylated guanosine triphosphate.
No such cap is formed at 5’end of bacterial mRNA.
8. In eukaryotes 5’cap initiates translation by binding mRNA
to small ribosomal subunit usually at the first codon AUG.
In bacteria translation begins at an AUG codon preceded by a
special nucleotide sequence.
9. A poly A tail formed of about 200 adenine nucleotides is
added at the 3’end of mRNA in Eukaryotes.
No poly A tail is added to bacterial mRNA.
10. In eukaryotes small subunit of ribosome(40 S) gets
dissociated with the initatior amino acyl tRNA (Met-tRNA Met) without the help
of mRNA. The complex joins mRNA later on.
In prokaryotes 30 S subunit first complexes with mRNA
(30S-mRNA) then joins with f Met tRNA f-Met.
Learn more: Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Protein Synthesis

.gif)
Very nice article. I certainly appreciate this site.
ReplyDeleteKeep it up!
Good post. I definitely love this website. Continue the good work!
ReplyDeleteSaved as a favorite, I love your blog!
ReplyDeleteGood post. I certainly appreciate this site.
ReplyDeleteKeep it up!
Thanks For Sharing this post with us.
ReplyDeleteBruh why'd all the comments get deleted
ReplyDeleteMay be Spam
Delete