What are selectable markers? How are antibiotic resistance genes used as selectable markers?
Let’s begin with selectable
marker
What is a Selectable
marker in a vector?
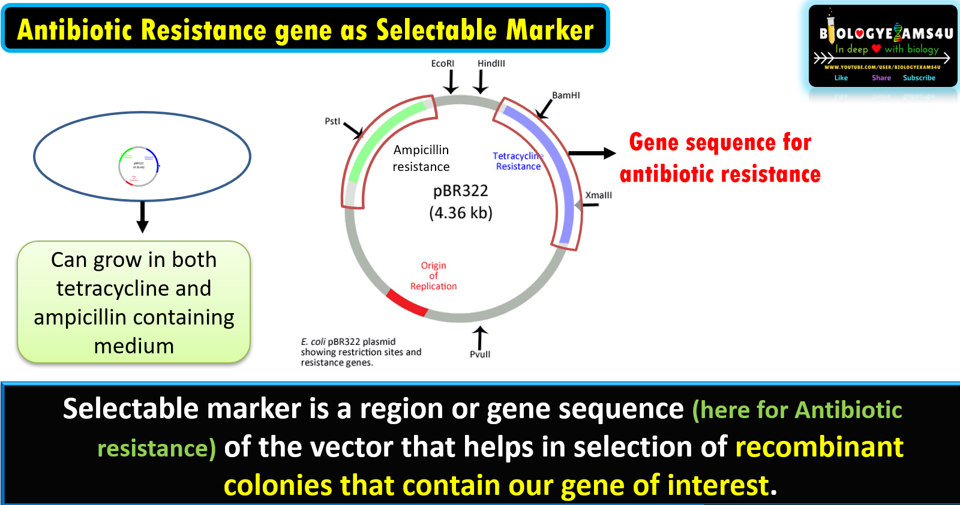
Selectable marker is a
region or gene sequence (here for Antibiotic resistance) of the vector that
helps in selection of recombinant colonies that contain our gene of interest.
You can also watch our video on Selectable markers at the end of this post for easy understanding.
Let’s take an example to understand this concept
An example is the use of pBR322, which has genes that encodes polypeptides which confer resistance to ampicillin and tetracycline antibiotics. That means a bacterium with this vector can grow both tetracycline and ampicillin containing medium.
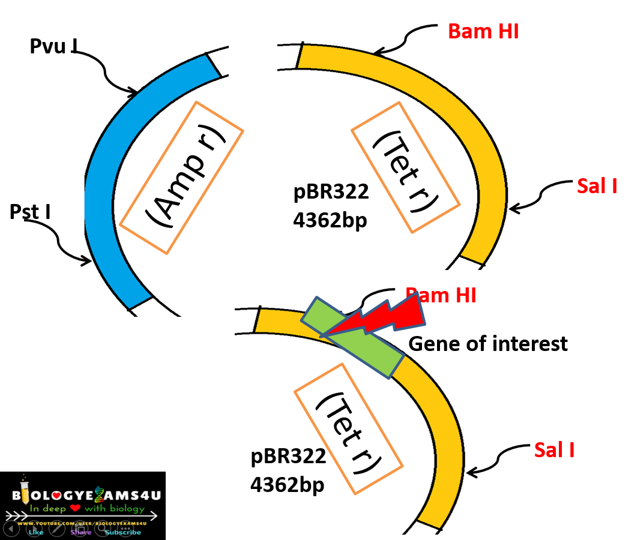
In the given example (figure above), we have inserted our gene of interest in the tetracycline gene coding region. So that, tetracycline resistance gene is no more functional. This process is called insertional inactivation.
What is Insertional inactivation?
Inactivation of a gene upon insertion of another
gene within its gene sequence.
The inserted gene disrupts continuity of the gene
sequence, thereby making it inactive or non-functional.
Watch this 5-minute video for better understanding.