Two types of conservation methods are prevalent. They are:
1. In-situ conservation method in which organisms are protected in their natural habitats
2. Ex-situ conservation method in which organisms are protected outside their natural habitats.
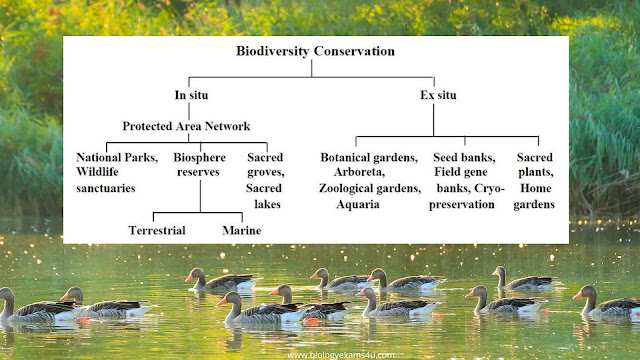
1. In-situ conservation
- Wild Life Sanctuary: These are forest areas declared as protected areas to prevent the extinction of wild lives by protecting the ecosystem.
- National Parks are designed to protect wild lives along with the protection of historical monuments, natural resources and geographical features of an area.
- Community reserves are areas protected with the participation of the public. These are ecologically important places located in populated areas.
- Biosphere reserves :These are vast regions designed with an aim to protect world's important ecosystems, biodiversity and genetic resources.
- Sacred groves: These are small areas of biodiversity protected in regions inhabited by human beings. Due to changes in life style many of these which were highly bio-rich have been destroyed. Only a few are remaining now. Sacred groves play an important role in the conservation of water in the region too.
- Ecological hotspots are areas rich in endemic species but facing the threat of habitat destruction. Each hotspot is ecologically a very important area of biodiversity. Out of the 34 hotspots all over the world, 3 of them are in India. They are the Western Ghats, North-Eastern Himalayas and the Indo-Burma region.
2. Ex-situ conservation
- Zoological gardens are conservation centres where different varieties of animals are protected and housed separately and where necessary arrangements are made available for their reproduction. They also function as conservation centres of organisms which have become extinct in wild.
- Botanical gardens These are wide research centres where rare and important plants of diverse species are protected.
- Gene Banks These are research centres with facilities to collect seeds and gametes to preserve them for a long time. Organisms can be recreated out of them whenever required.
Summary
.jpg)
Biodiversity conservation may be in situ as well as ex situ. In in situ conservation, the endangered species are protected in their natural habitat so that the entire ecosystem is protected. Recently, 34 ‘biodiversity hotspots’ in the world have been proposed for intensive conservation efforts. Of these, three (Western Ghats-Sri Lanka, Himalaya and Indo-Burma) cover India’s rich biodiversity regions. Our country’s in situ conservation efforts are reflected in its 14 biosphere reserves, 90 national parks, > 450 wildlife sanctuaries and many sacred groves. Ex situ conservation methods include protective maintenance of threatened species in zoological parks and botanical gardens, in vitro fertilisation, tissue culture propagation and cryopreservation of gametes.
